Aspirin
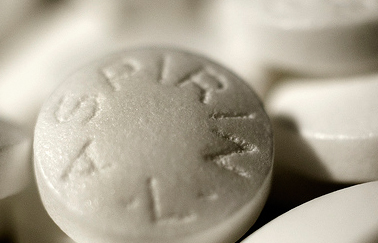
Acetylsalicylic acid, also known as aspirin, is an acetyl derivate of salicylic acid, which is a weak white and crystalline acidic substance, that has a melting point of 135-137oC.

Acetylsalicylic acid, also known as aspirin, is an acetyl derivate of salicylic acid, which is a weak white and crystalline acidic substance, that has a melting point of 135-137oC.
AIMS:
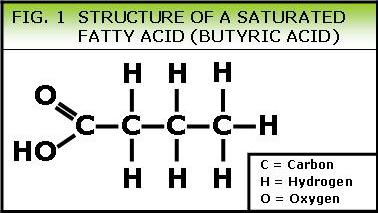
To revise and extend students’ knowledge of butyric carbohydrates
To systemize students’ knowledge of butyric carbohydrates
To put into practice the acquired knowledge of the structure, isomerism and chemical properties of the butyric carbohydrates
To illustrate the connection between the carbohydrates by means of chemical reactions
To develop students’ thinking and imagination by means of different logical operations- synthesis, analysis, comparison, analogy

AIMS:
To revise and extend students’ knowledge of butyric carbohydrates
To systemize students’ knowledge of butyric carbohydrates
To put into practice the acquired knowledge of the structure, isomerism and chemical properties of the butyric carbohydrates
To illustrate the connection between the carbohydrates by means of chemical reactions
To develop students’ thinking and imagination by means of different logical operations- synthesis, analysis, comparison, analogy
1. What is the chemical bond?
2. What is the function of the chemical bond?
3. What types of chemical bonds do you know?

LEARNING OBJECTIVES
? to define a chemical change
? to recognize a chemical change and distinguish it from a physical one
? to read a chemical equation
? to write chemical equations
? to balance chemical equations
? to classify chemical reactions
? to write formation and combustion reactions for given compounds.
? to recognize the limitant reactant
? to make stoichiometric calculations:
from mass to moles, from moles to mass,
yield, masses needed for complete reactions (from a given quantity of a reactant)
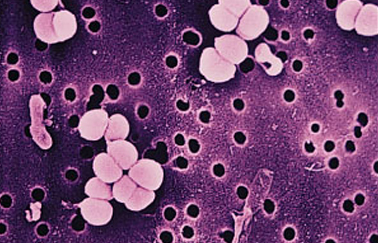
Objective of the activity is to determine the quality of water samples of different sources using chemical and microbiological indirect methods. The action has planned activities in the laboratory of Chemistry with the determination of the presence of the organic substance, as an indicator of contamination, through the method of Kubel and in the laboratory of Microbiology with the determination of Total Coliforms with MPN method.