Periodic Table

Procedures:
1.Students are given the definitions of Group and Period s.
2.They are taught systematic variying features at the Periodic Table.
3.Groups of A and B and their features are told.

Procedures:
1.Students are given the definitions of Group and Period s.
2.They are taught systematic variying features at the Periodic Table.
3.Groups of A and B and their features are told.
Lesson Objectives :
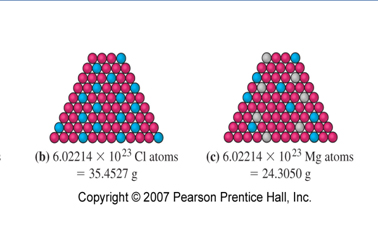
1)To Explain the mole concept with the particle concept and the number of Avogadro
2)To use ICT as a succesful tool when learning.
Method : Question – Answer Method,grup discussion, teaching method
AIMS:
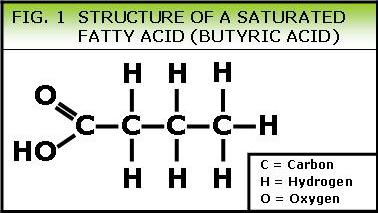
To revise and extend students’ knowledge of butyric carbohydrates
To systemize students’ knowledge of butyric carbohydrates
To put into practice the acquired knowledge of the structure, isomerism and chemical properties of the butyric carbohydrates
To illustrate the connection between the carbohydrates by means of chemical reactions
To develop students’ thinking and imagination by means of different logical operations- synthesis, analysis, comparison, analogy

Some Information about luminol
IUPAC name: 5-amino-2,3-dihydro-1,4-phtalazinedione
Molar mass:
177,16 g/mol
Melting point:
319 – 320 °C
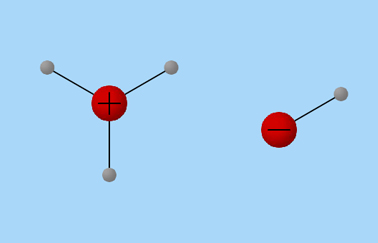
Definition: The molar heat of neutralizing represents the quantity of heat given up when a mole of a hydronium ion interacts with a mole of hydroxyl ion in a diluted solution.
Lesson Objectives
1. To be able to write the name of the ionic compound the formula of which is given.
2. To be able to write formula of the ionic compound the name of which is given.
3. To be able to write the name of the covalent compound the formula of which is given.
4. To be able to write the formula of the covanlent compound the name of which is given.
5. To use ICT as a successful tool when learning.